What is Software Engineering?
The term Software Engineering is the product of two words, software, and engineering.It is a collection of integrated programs.Software subsists of carefully-organized instructions and code written by developers on any of various particular computer languages.Computer programs and related documentation such as requirements, design models and user manuals.Engineering is the application of scientific and practical knowledge to invent, design, build, maintain, and improve frameworks, processes, etc.
Software Engineering is an engineering branch related to the evolution of software product using well-defined scientific principles, techniques, and procedures. The result of software engineering is an effective and reliable software product.
Why is Software Engineering required?
Software Engineering is required due to the following reasons:
Need of Software Engineering
The necessity of software engineering appears because of a higher rate of progress in user requirements and the environment on which the program is working.
Process Models
Waterfall Model
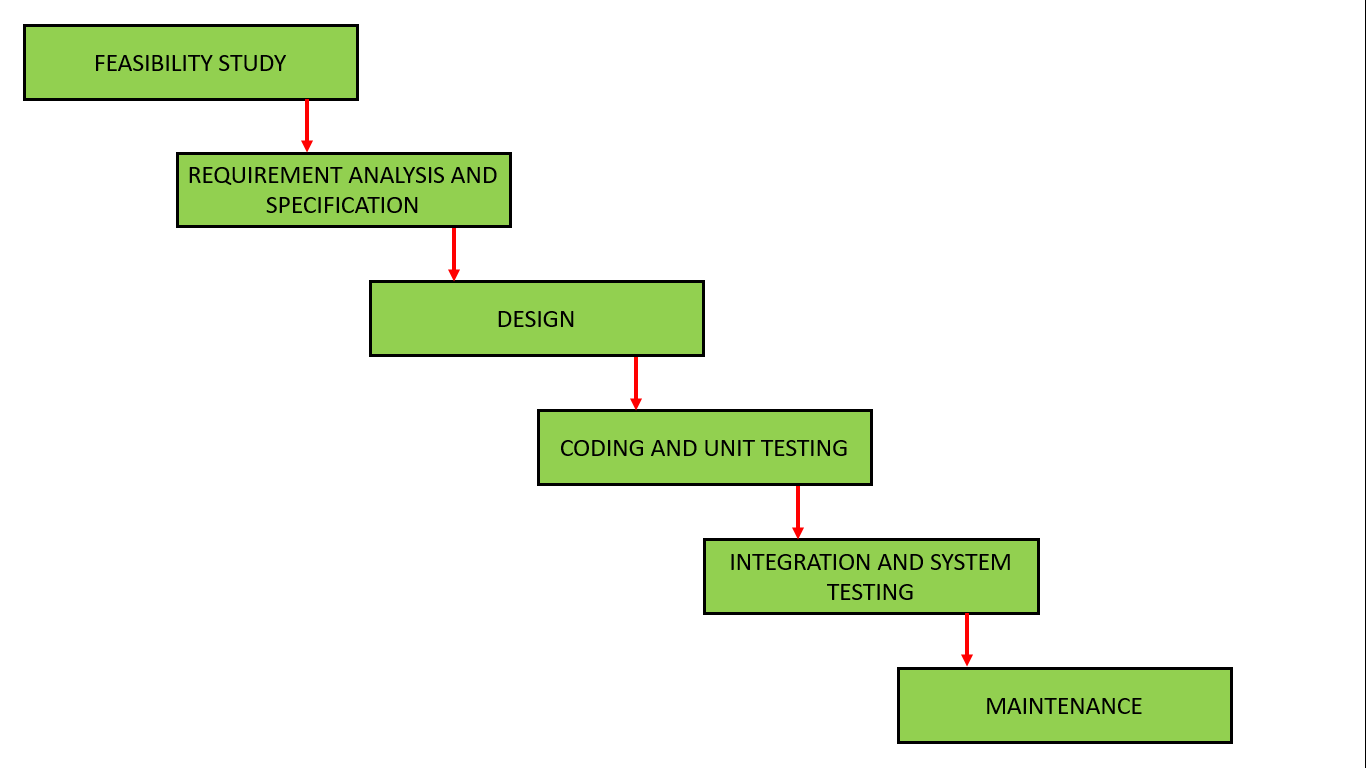
Phases of Waterfall ModelWaterfall Model is a classical software development methodology that was first introduced by Winston W. Royce in 1970. It is a linear and sequential approach to software development that consists of several phases that must be completed in a specific order.
The Waterfall Model has six phases:
1. Requirements Gathering and Analysis:
The first phase involves gathering requirements from stakeholders and analyzing them to understand the scope and objectives of the project.
2. Design Phase:
Once the requirements are understood, the design phase begins. This involves creating a detailed design document that outlines the software architecture, user interface, and system components.
3. Implementation and Unit Testing:
The implementation phase involves coding the software based on the design specifications. This phase also includes unit testing to ensure that each component of the software is working as expected.
4. Integration and System Testing:
In the testing phase, the software is tested as a whole to ensure that it meets the requirements and is free from defects.
5. Deployment:
Once the software has been tested and approved, it is deployed to the production environment.
6. Maintenance:
The final phase of the Waterfall Model is maintenance, which involves fixing any issues that arise after the software has been deployed and ensuring that it continues to meet the requirements over time.
Spiral Model
Phases of Spiral Model
The Spiral Model is a risk-driven model, meaning that the focus is on managing risk through multiple iterations of the software development process. It consists of the following phases:
1. Planning
first phase of the Spiral Model is the planning phase, where the scope of the project is determined and a plan is created for the next iteration of the spiral.
2. Risk Analysis
In the risk analysis phase, the risks associated with the project are identified and evaluated.
3. Engineering
In the engineering phase, the software is developed based on the requirements gathered in the previous iteration.
4. Evaluation
In the evaluation phase, the software is evaluated to determine if it meets the customer’s requirements and if it is of high quality.
5. Planning
The next iteration of the spiral begins with a new planning phase, based on the results of the evaluation.
The Spiral Model is often used for complex and large software development projects, as it allows for a more flexible and adaptable approach to software development. It is also well-suited to projects with significant uncertainty or high levels of risk.
The Radius of the spiral at any point represents the expenses(cost) of the project so far, and the angular dimension represents the progress made so far in the current phase.

Each phase of the Spiral Model is divided into four quadrants as shown in the above figure. The functions of these four quadrants are discussed below:
- Objectives determination and identify alternative solutions: Requirements are gathered from the customers and the objectives are identified, elaborated, and analyzed at the start of every phase. Then alternative solutions possible for the phase are proposed in this quadrant.
- Identify and resolve Risks: During the second quadrant, all the possible solutions are evaluated to select the best possible solution. Then the risks associated with that solution are identified and the risks are resolved using the best possible strategy. At the end of this quadrant, the Prototype is built for the best possible solution.
- Develop the next version of the Product: During the third quadrant, the identified features are developed and verified through testing. At the end of the third quadrant, the next version of the software is available.
- Review and plan for the next Phase: In the fourth quadrant, the Customers evaluate the so-far developed version of the software. In the end, planning for the next phase is started.
Agile Model
Phases of Agile Model:
Following are the phases in the Agile model are as follows:
1. Requirements gathering:
In this phase, you must define the requirements. You should explain business opportunities and plan the time and effort needed to build the project. Based on this information, you can evaluate technical and economic feasibility.
2. Design the requirements:
When you have identified the project, work with stakeholders to define requirements. You can use the user flow diagram or the high-level UML diagram to show the work of new features and show how it will apply to your existing system.
3. Construction/ iteration:
When the team defines the requirements, the work begins. Designers and developers start working on their project, which aims to deploy a working product. The product will undergo various stages of improvement, so it includes simple, minimal functionality.
4. Testing:
In this phase, the Quality Assurance team examines the product's performance and looks for the bug.
5. Deployment:
In this phase, the team issues a product for the user's work environment.
6. Feedback:
After releasing the product, the last step is feedback. In this, the team receives feedback about the product and works through the feedback.